Unlocking Strength and Precision: The Benefits of Diffusion Bonding in Modern Manufacturing
For advanced manufacturing, where precision, durability, and performance are paramount, diffusion bonding has emerged as a critical process for creating superior metal joints. Unlike traditional welding or brazing, diffusion bonding operates without melting the materials. Instead, it forges high-strength bonds at the atomic level, making it an indispensable technique in industries where failure is not an option.
What Is Diffusion Bonding?
Diffusion bonding is a solid-state joining process that involves pressing two surfaces together under high temperature and pressure for a prolonged period. During this process, atoms from each surface migrate across the interface, creating a bond that can be as strong as or even stronger than the parent materials. Importantly, this is achieved without any melting, filler materials, or external agents.
The Strength Advantage: High-Integrity Joints
One of the most compelling benefits of diffusion bonding is the creation of exceptionally strong and reliable joints. Because the bond forms at the atomic level and involves no phase change, the integrity of the material is preserved. There is minimal microstructural disruption, which translates into joints with high mechanical strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and superior performance under stress.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Traditional welding methods often struggle to join dissimilar metals due to differences in melting points and thermal expansion coefficients. Diffusion bonding, on the other hand, excels in this area. It enables the effective joining of challenging material combinations such as titanium to stainless steel or metals to ceramics. This capability significantly expands design and engineering possibilities, particularly in aerospace, medical, and nuclear applications.
Purity and Cleanliness: No Fillers or Flux
Another significant advantage of diffusion bonding is its clean process. The absence of filler materials, fluxes, or external binding agents means there is less risk of contamination. This makes diffusion bonding especially suitable for applications where purity is critical, such as in semiconductor manufacturing or medical device fabrication.
Dimensional Accuracy and Minimal Distortion
Because the materials do not melt, diffusion bonding avoids many of the pitfalls associated with heat-based joining methods, such as warping, shrinkage, or residual stresses. This results in exceptional dimensional accuracy, making it the go-to choice for precision assemblies. Components such as microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), intricate turbine parts, and fine instrumentation rely heavily on this advantage.
Complex Assemblies and Miniaturization
As technology advances, the demand for smaller, more complex components continues to grow. Diffusion bonding meets this need by facilitating the joining of intricate or multi-layered components, such as laminated heat exchangers or fuel cell plates. Its precision and strength enable the miniaturization of high-performance assemblies without compromising structural integrity.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Applications in aerospace, defense, and energy require materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and environmental conditions. Diffusion bonded parts exhibit outstanding performance under such conditions due to their high creep resistance, fatigue endurance, and thermal stability. These qualities make them indispensable in jet engines, nuclear reactors, and high-performance electronics.
Industry Applications: A Cross-Sector Solution
- Aerospace: Titanium and nickel alloy components in turbine engines and structural assemblies.
- Medical: High-strength, bio-compatible implant assemblies and surgical instruments.
- Electronics: Precision microfluidic and MEMS devices.
- Energy: Durable components in nuclear reactors and high-efficiency heat exchangers.
Conclusion
Diffusion bonding represents a fusion of science and engineering that enables manufacturers to meet the demands of tomorrow's technology. With its unmatched strength, precision, and versatility, diffusion bonding is not just a joining method—it's a cornerstone of innovation. As industries continue to evolve and push the boundaries of performance and miniaturization, diffusion bonding will remain a vital enabler of progress.
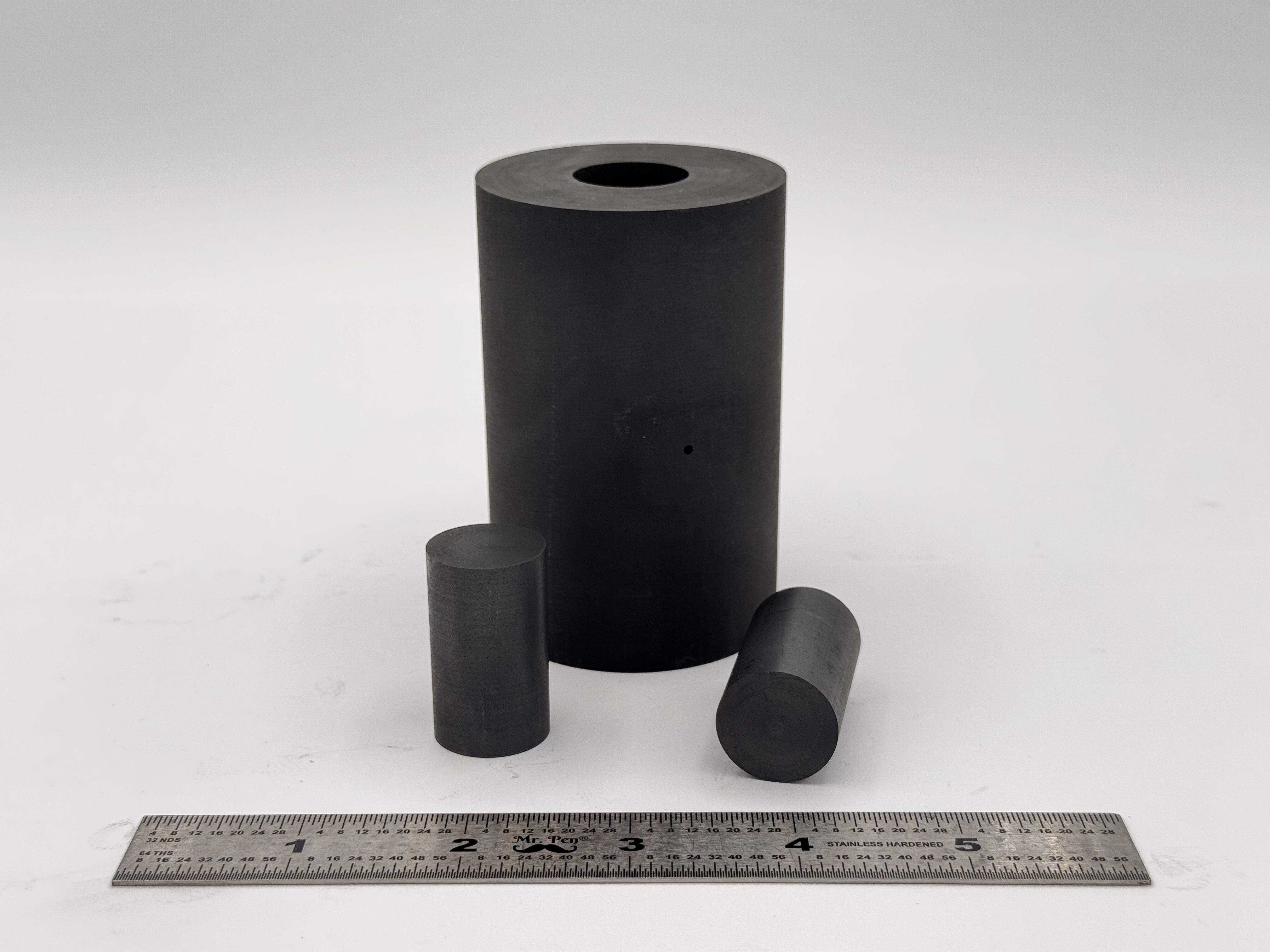 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling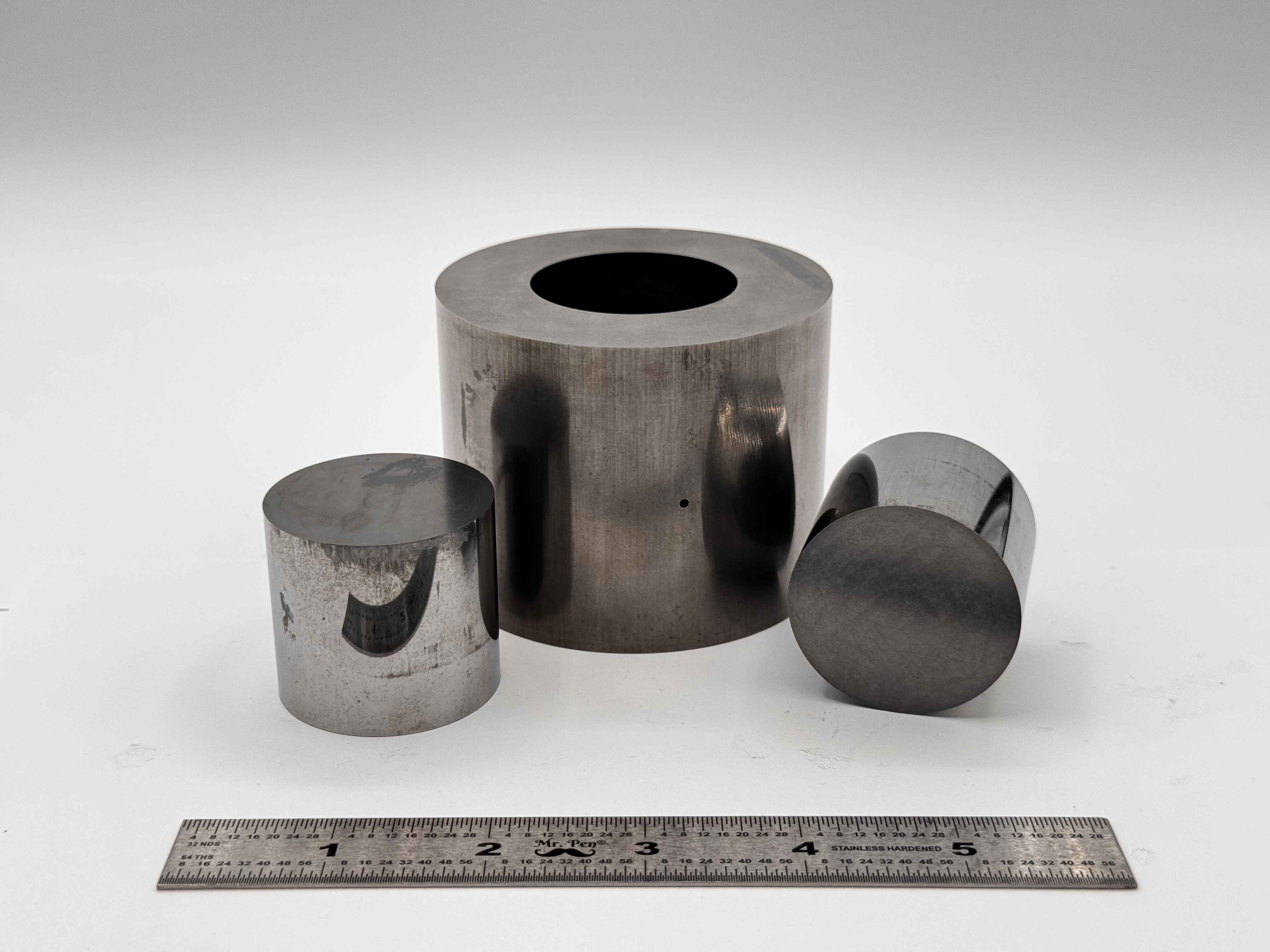 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software