What is Advanced Hot Pressing?
Advanced hot pressing is a highly specialized manufacturing technique used to create dense, high-performance materials by applying both heat and pressure simultaneously. This process, an enhancement over conventional hot pressing, is particularly effective for forming metals, ceramics, and composite materials into durable, reliable components with superior structural integrity. Its ability to produce parts with minimal porosity and excellent mechanical properties makes it essential in critical industries such as aerospace, defense, and energy.
How Advanced Hot Pressing Works
The process of advanced hot pressing begins with the preparation of raw materials, typically in the form of powder. This powder is carefully placed into a die, which is then subjected to high temperatures (often exceeding 1000°C) and uniaxial pressure. The dual action of heat and pressure causes the powder particles to bond tightly, significantly reducing voids and creating a dense, uniform material.
To ensure optimal material quality, the entire process takes place in a controlled atmosphere—often under vacuum or inert gas—to prevent contamination or oxidation during sintering. This meticulous approach allows for precise control over the microstructure and properties of the finished component.
Key Advantages of Advanced Hot Pressing
Advanced hot pressing provides several notable benefits over traditional sintering or pressing techniques:
- Superior Densification: Achieves near-theoretical density, resulting in robust and durable parts.
- Shorter Sintering Cycles: Significantly reduces the time required to achieve full densification compared to pressureless sintering.
- Lower Temperatures: Pressure-assisted sintering allows for effective bonding at relatively lower temperatures.
- Fine Microstructures: Produces uniform, fine-grained materials with improved mechanical characteristics.
These advantages make advanced hot pressing ideal for manufacturing components that demand the highest level of reliability and performance.
Applications Across Industries
Because of its ability to produce high-density, high-strength parts, advanced hot pressing is widely used in:
- Aerospace – For structural components and heat-resistant materials.
- Defense – In the production of ceramic armor and ballistic plates.
- Nuclear Energy – For fabricating high-performance fuel pellets and reactor components.
- Tooling and Manufacturing – To create wear-resistant cutting tools and dies.
- Automotive and Electronics – In high-performance components requiring thermal and mechanical stability.
Advanced Variants and Technologies
Several modern variants of hot pressing have further expanded its capabilities:
- Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): Integrates pulsed DC current with pressure to achieve rapid and uniform heating, drastically shortening processing times.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Uses inert gas to apply uniform pressure in all directions, ideal for complex or delicate geometries.
- Field-Assisted Sintering Techniques (FAST): Incorporates electric or magnetic fields to enhance sintering efficiency and control.
These innovations allow manufacturers to tailor the process to specific materials and applications, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in advanced materials science.
Conclusion
Advanced hot pressing stands at the forefront of high-performance material manufacturing. By uniting the power of heat and pressure under controlled conditions, it enables the production of components with exceptional strength, density, and durability. Whether used in aerospace engineering or advanced tooling, this process ensures that manufacturers can meet the most stringent quality and performance standards.
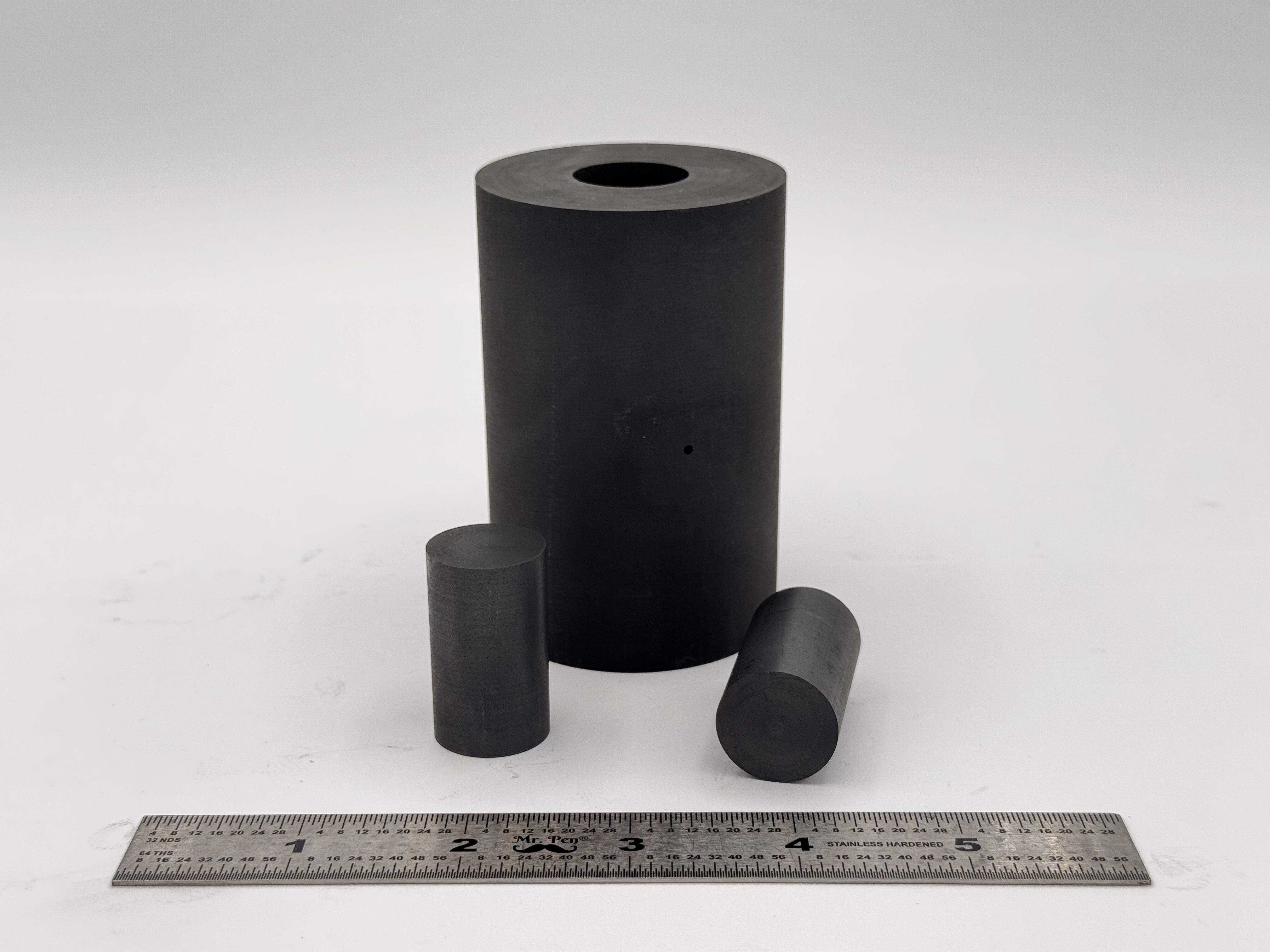 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling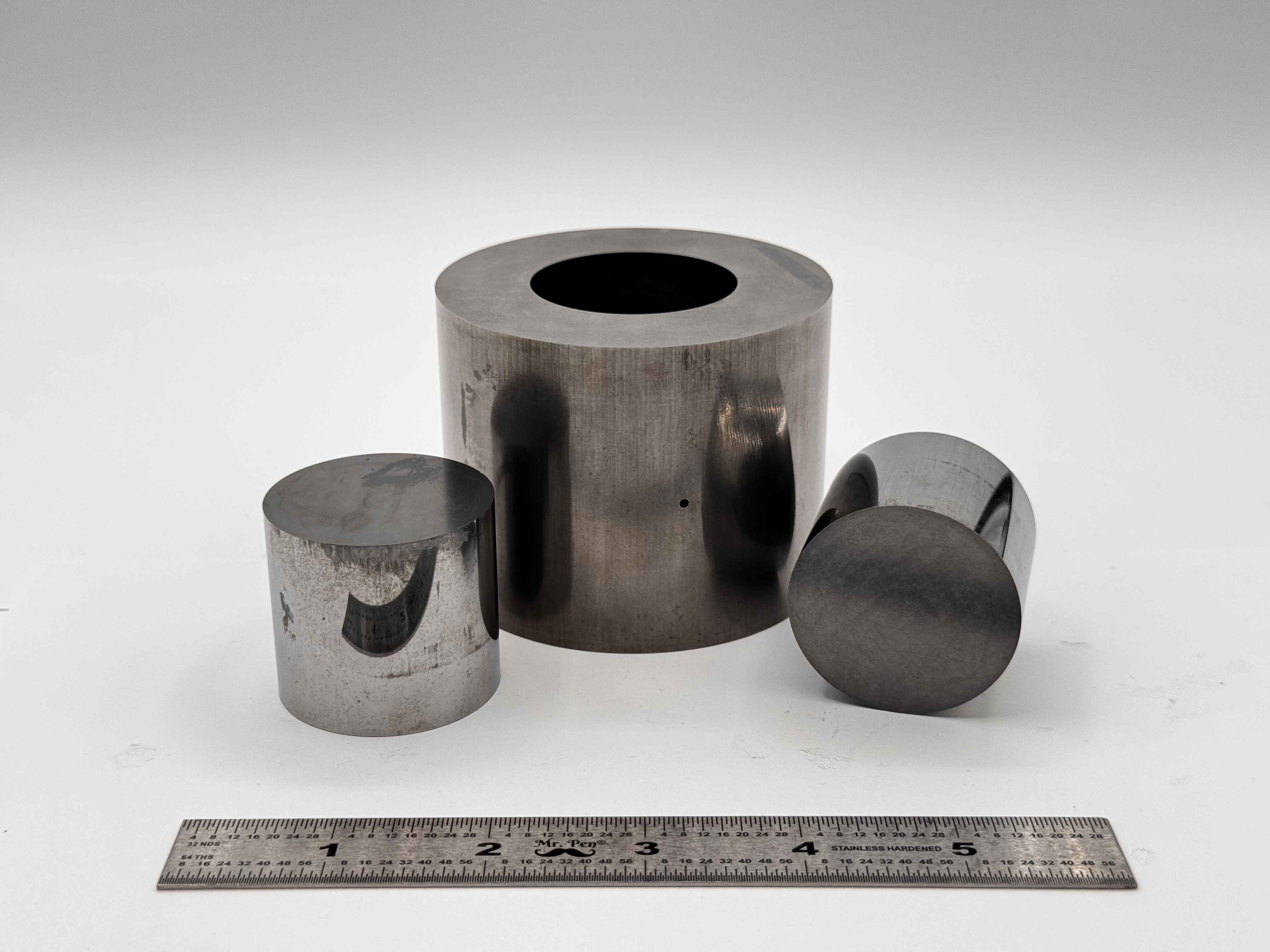 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software