Revolutionizing Materials Synthesis: An In-Depth Exploration of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a powder metallurgy technique used for the densification of materials, particularly ceramics and powder-based materials. It is also known as Field Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST). The process involves the application of both pressure and pulsed direct current (DC) or pulsed alternating current (AC) to the powder compact during the sintering process.
Key components of Spark Plasma Sintering:
Powder Preparation:
- The process typically starts with the preparation of a powder mixture consisting of the desired materials.
Die Filling:
- The powder is then placed in a die, forming a compacted shape.
Application of Pressure:
- A uniaxial pressure is applied to the powder compact to ensure good contact between the powder particles.
Application of Electric Field:
- A pulsed direct current or alternating current is applied to the powder compact. This electric field promotes the movement of atoms or ions, resulting in enhanced diffusion and sintering.
Heating:
- Simultaneously, the sample is heated. The combination of pressure, electric field, and heat helps in the rapid and uniform densification of the material.
Sintering:
- The simultaneous application of pressure and electric field reduces the sintering temperature and time compared to traditional sintering methods. This leads to the creation of a dense material with improved mechanical and thermal properties.
Spark Plasma Sintering has several advantages, including the ability to achieve high-density sintered materials with fine microstructures, reduced sintering times, and the possibility of sintering materials that are challenging to sinter using conventional methods.
It finds applications in various fields, including the fabrication of advanced ceramics, composites, and other high-performance materials. The process is particularly useful for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures and for producing components with unique properties.
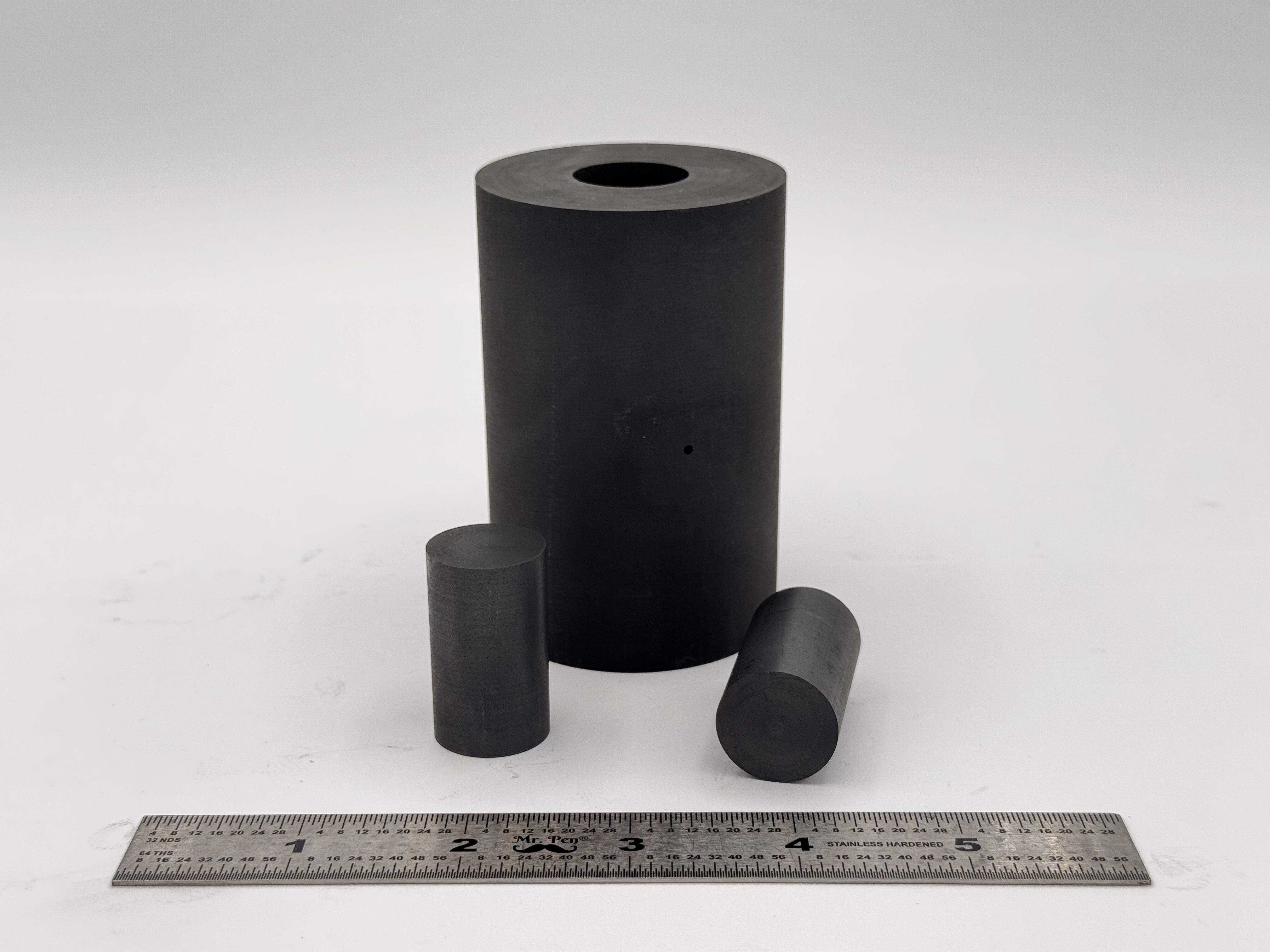 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling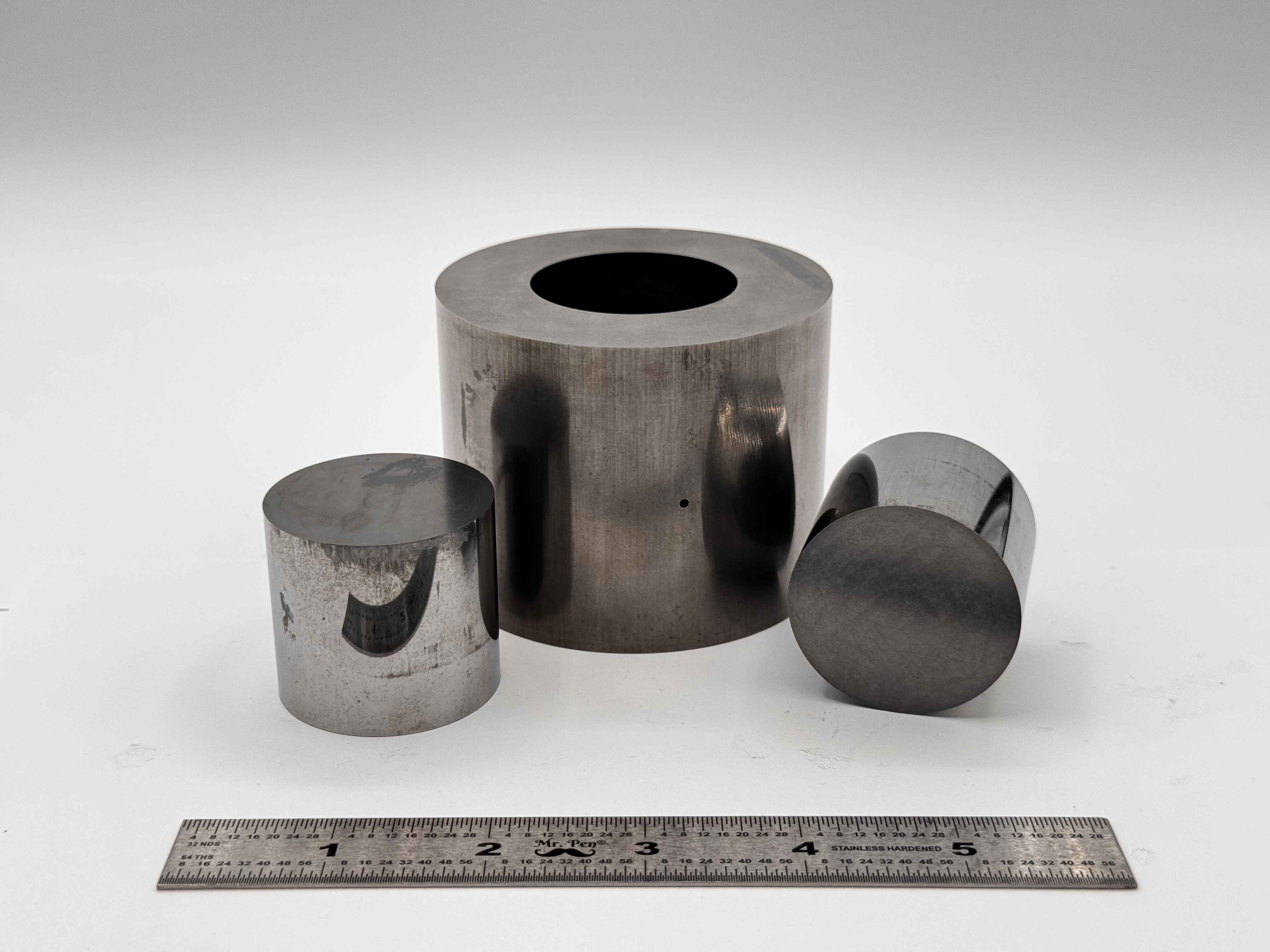 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software