Understanding SPS Machines: Their Role in Modern Industry
In today's fast-paced world of manufacturing and industry, automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, productivity, and precision. One such marvel of automation is the SPS machine, which stands for "Sequential Programmed System." These machines are integral components of various industrial processes, making them more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective.
What is an SPS Machine?
SPS machines, or Sequential Programmed Systems machines, are devices designed to automate and control a wide range of industrial processes. They are often referred to as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in industrial automation contexts. These machines are electronic devices that follow pre-programmed sequences to perform specific tasks, making them an indispensable tool in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, food processing, and more.
Key Components of an SPS Machine
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The heart of the SPS machine is its CPU, which processes the program logic and control instructions.
- Input/Output Modules (I/O Modules): These modules are responsible for interfacing with the external world. They read data from sensors and send control signals to actuators, facilitating communication between the machine and the industrial process.
- Memory: SPS machines have both RAM and ROM memory. ROM stores the program's logic and instructions, while RAM temporarily stores data and variables used during the operation.
- Programming Interface: Engineers and technicians program SPS machines using dedicated software, specifying the sequence of actions, logic, and conditions for the machine to follow.
How SPS Machines Work
SPS machines follow a set of programmed instructions to perform various tasks. The programming involves specifying the conditions that trigger specific actions, the order in which these actions occur, and how the machine should respond to variations or errors in the process. This makes SPS machines incredibly versatile and adaptable to different industrial applications.
SPS machines operate based on a scan cycle. During each cycle, the machine reads input data from sensors, processes this information, executes the programmed logic, and sends control signals to actuators. This cycle repeats continuously, allowing the SPS machine to maintain real-time control over the industrial process.
Applications of SPS Machines
SPS machines find applications in a wide range of industries, serving various purposes. Some common applications include:
- Manufacturing: SPS machines control assembly lines, robotics, conveyors, and quality control systems, ensuring seamless and precise production processes.
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, SPS machines manage tasks such as engine control, car body assembly, and quality assurance.
- Food Processing: SPS machines are vital in food manufacturing, regulating processes like packaging, sorting, and temperature control.
- Energy: SPS machines manage power distribution, grid control, and renewable energy systems.
- Water Treatment: In water treatment facilities, SPS machines regulate the purification process, chemical dosing, and wastewater management.
Benefits of SPS Machines
SPS machines offer numerous advantages to industries:
- Precision: They provide precise control over processes, reducing errors and waste.
- Efficiency: SPS machines work tirelessly, 24/7, optimizing productivity and minimizing downtime.
- Flexibility: They can be reprogrammed for different tasks, making them adaptable to changing production needs.
- Reliability: SPS machines are robust and durable, ensuring consistent performance in challenging industrial environments.
- Safety: SPS machines can be programmed to detect and respond to safety hazards, protecting both machinery and workers.
Conclusion
SPS machines, or Sequential Programmed Systems machines, are the unsung heroes of modern industry. Their ability to automate and control a vast array of industrial processes makes them invaluable in the pursuit of efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness. As technology continues to advance, SPS machines are expected to play an increasingly prominent role in the industrial landscape, driving innovation and progress in countless sectors.
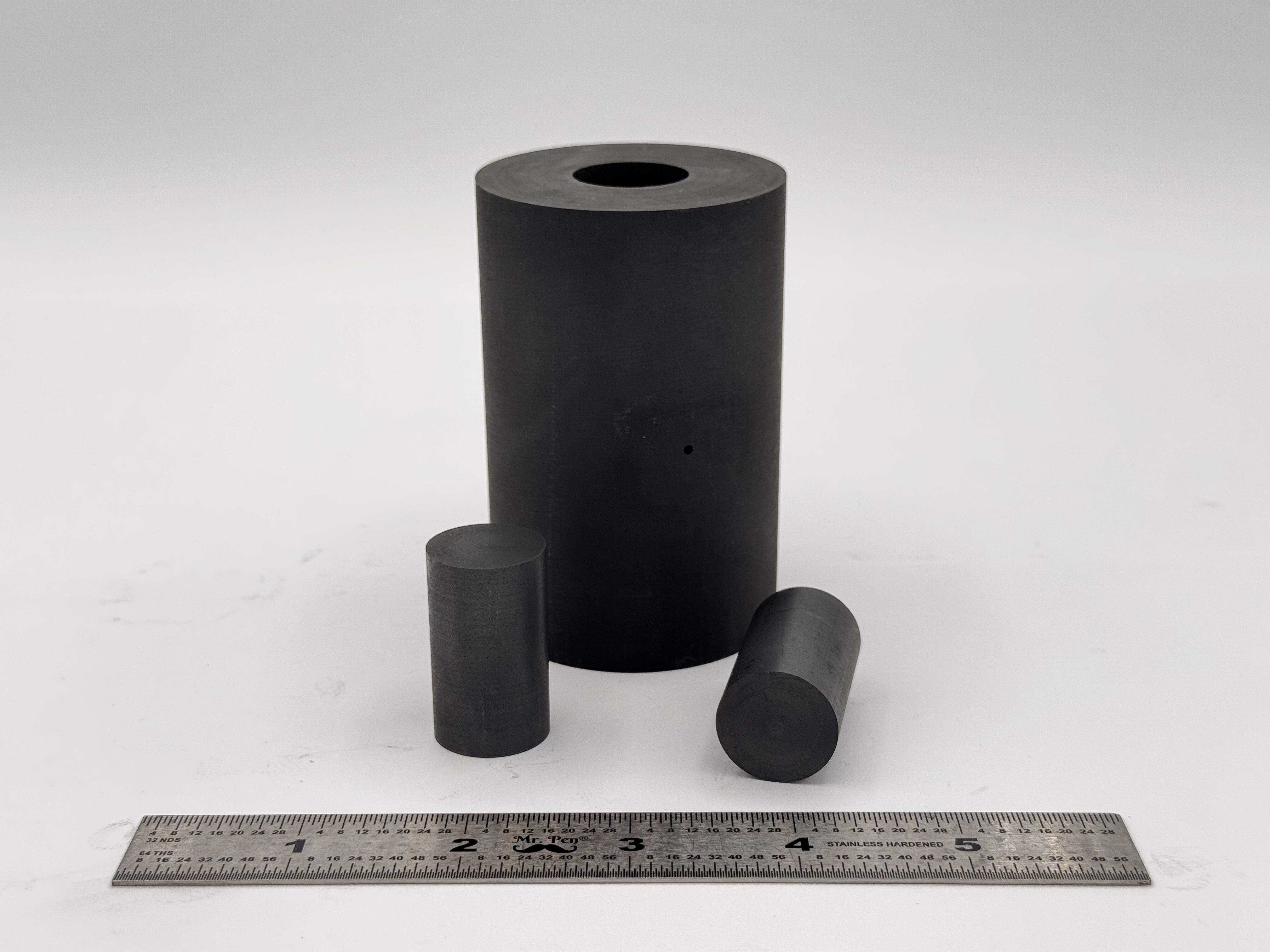 High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling
High Strength SPS Graphite Tooling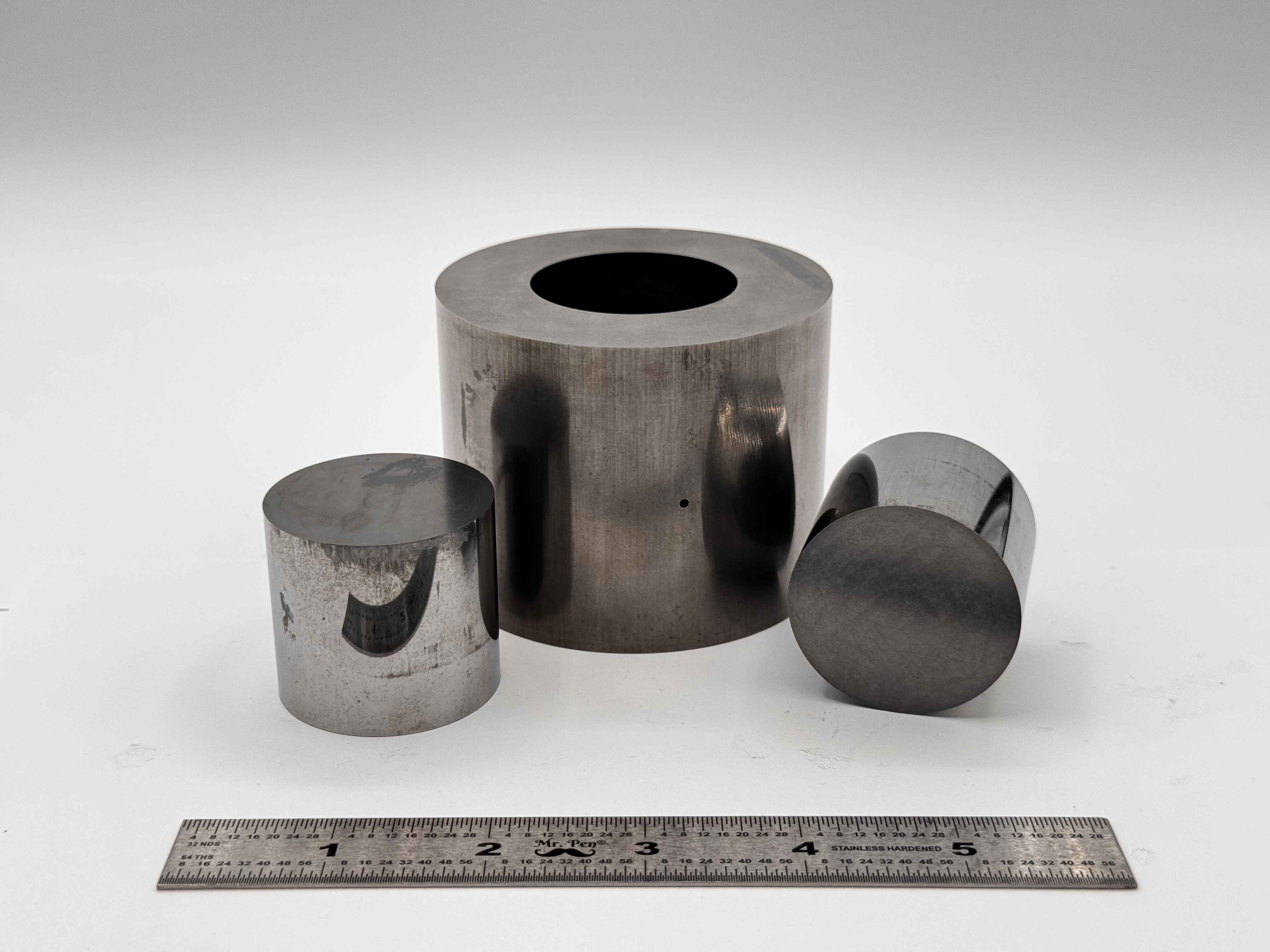 Tungsten Carbide Tooling
Tungsten Carbide Tooling Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper
Carbon Graphite Foil / Paper Carbon Felt and Yarn
Carbon Felt and Yarn Spark Plasma Sintering Systems
Spark Plasma Sintering Systems SPS/FAST Modeling Software
SPS/FAST Modeling Software